How to Configure Routing RIPng, EIGRPv6 and OSPFv3 for IPV6
Configure Routing with IPv6
In IPv6 we use the same type of Routing Protocols that were used with IPv4 but has some changes so they can meet the requirements of IPv6.
The below are types of routing supported in IPv6.
- Static
- RIPng (RFC 2080)
- IS-IS for IPv6
- OSPFv3 (RFC 2740)
- MP-BGP
- EIGRP for IPv6
In this article we will cover, RIPng, EIGRPv6 and OSPFv3 for IPv6.
The Cisco Routers would have IPv6 disabled by default and will need to have it enabled using the below command. The “ipv6 unicast-routing” command should be executed globally on all routers that need to participate in IPv6.
# ipv6 unicast-routing
# interface type [slot number] / port number
# ipv6 address <ipv6_address_prefix/prefix length> [eui-64]
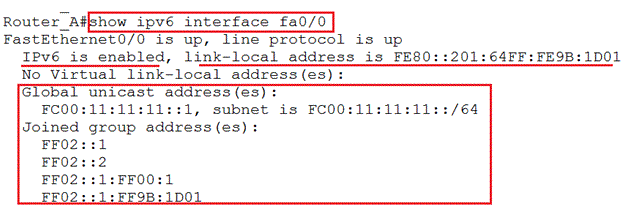
The command “show ipv6 interface” will display the interface configuration which is used for verifying if the configuration is correct.
See the below topology:
RIPng
Routing Information Protocol next Generation (RIPng) is similar to the RIP we used in IPv4. Below are its characteristics:
- Distance Vector Protocol
- Max hop count is 15
- Uses split horizon and poison reverse to avoid routing loops
- IPv6 uses RIPv2
- The routing update is transported using IPv6 Packet
- The destination address used in routing is ALL RIP Routers Multicast(FF02::9) and
EIGRPv6
As RIPng, EIGRPv6 also work pretty the same way as EIGRP v4.
- EIGRPv6 is an advance distance Vector Protocol along with Link state capabilities and thus known as HYBRID protocol
- Reliable Transport Protocol is used for reliable communication
- The algorithm used is DUAL (Diffusing Update Algorithm)
- Multicast Address for EIGRPv6 is FF02::A
The configuration looks as below:
Here in the above command 100 is the AS number.
OSPFv3
Same as other Protocols OSPFv3 also is similar to its IPv4 version.
- It is a link state protocol
- Uses the SPF algorithm to calculate the shortest path
- Uses the concepts of Areas to divide the network
- In OSPFv3, we need to manually configure the Router ID, area ID and link-state ID.
- Multicast FF02::5 is used for OSPF Routers
- Multicast FF02::6 is used for OSPF Designated Routers
The configuration is as below:
We just need to configure the router id and the area id for the interface and the configuration is done.