IP Address Classes
What are IP Address Classes?
IP Address Classes are the scheme that divides IP addresses into different ranges, and allows them to be shared by organizations of different sizes. To do it, they also define the purposes of the classes of IP addresses, and that’s how they can be sorted out between those for organizations, those for the networks, and those that have experimental purposes.
This addressing scheme is sometimes defined as “classful”, to tell it apart from the newer, IPv6 classless scheme.
IP Address Classes were designed by IANA (Internet Assigned Number Authority), due to the expected requirements of the newborn, fast growing Internet, and, as the Internet expanded, the task to regulate and distribute them passed to ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers), created for that purpose, and to take on IANA previous responsibilities.
The IP software can deduce classes by the first binary digits of a IP address (high order bits), that start either with 0 or with 1, to determine things like logical network and host addresses.
The Five IP Address Classes
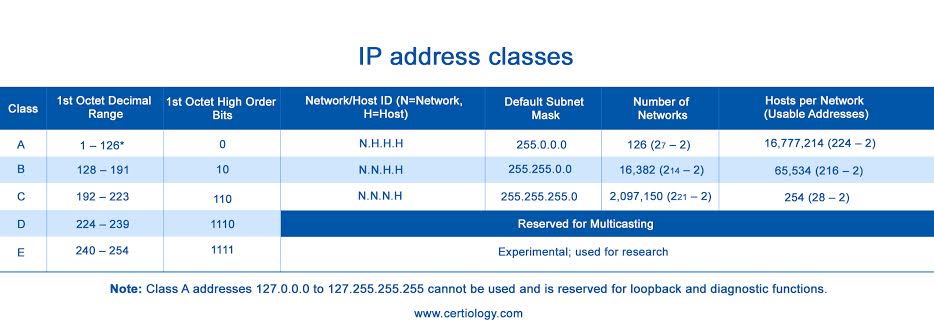
Class A: This is the first of the classes available to the public, with 128 networks in existence for the IPv4 classful scheme, all reserved for large organizations.
To identify it as Class A is the first bit in the IP address is 0, remaining octet bits that provide network identification, and the further 24 bits used for host-bit addressed, available for use to 16 million Class A network host Class A always has a number between 0 and 126 in the first octet, with 127 kept for loopback. Default subnet mask is 255.0.0.0.
Class B: The second class available to the public, for organizations of medium size, has the first two bits in the binary 1 0 format, and the other 14 bits of the two octets there for network addressing, and with the remaining 16 bits used for host addressing.
In the first octet, the number found is between 128 and 191. Default subnet mask 255.255.0.0.
Class C: Third class available to the public, and most common (roughly 16 millions of possible addresses), with 1 1 0 as the first bit of the IP address, other 21 bits used for network addressing, and the further 8 used for host addressing.
A number between 192 and 223 is found in the first octet. Default subnet mask 255.255.255.0.
Class D: First of the classes kept for special purposes, in this case for multicasting, the addressing of groups of IP devices at the same time, with 1 1 1 0 as the first bits in the first octet. Number found in the first octet ranger only from 224 to 239.
Class E: Other class not available to the public, kept for experimental purposes and research, and they were never documented. First four bits in the addressing are 1 1 1 1. Numbers range in the first octet is 240 to 254.
Free Practice Tests
- Free MTA Practice Tests and Exams
- Free MCSA Windows 7 Practice Tests and Exams
- Free MCSA Windows 8 Practice Tests and Exams
- Free MCSE and MCSA Windows Server 2012 Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CompTIA A+ Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- A+ Practice Test
- Free CompTIA CDIA+ Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CompTIA Linux+ Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CompTIA Network+ Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CompTIA Project+ Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CompTIA Security+ Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CompTIA Server+ Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CompTIA Storage+ Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CCENT 100-101 ICND1, CCNA 200-101 ICND2, 200-120 CCNA Practice Exams and Tests
- Free Cisco CCNA certification practice tests and Exams Questions
- Free CCNA Security Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CCNA Wireless Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CCNA Voice Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CCNP practice tests and Exams Questions
- Free CCIE Collaboration Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CCIE Routing and Switching Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CCIE Security Certification Practice Tests and Exams
- Free CCIE Wireless 350-050 Practice Exam