Basics of Virtualization
Basics of Virtualization
What does Virtualisation mean? The basic definition is ‘that which does not exist physically but is a process, system or computer which will act as a physical system You can operate it as a physical system. In virtualization, the CPU is known as a vCPU, and HDD as a vHDD.
After installing the Operating System (OS) in the virtual environment, the system is then called the VM (Virtual Machine), which accesses the network via the Physical Network Interface Card. VM also has its own Virtual Network Card known as vNIC. In your physical system, you can also install multiple OS with Virtualization. The most important thing to note is that the VM can access all hardware from the main physical machine.
These are the companies which provide the Virtualization technology at server level:
- Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2008 R2
- VMware vSphere 5.0
- Citrix XenServer
- Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization 3
For the Desktop user, and those who want to run Virtual Machines on a desktop or laptop, the providers are:
- Virtual Box
- VMware
- Windows Virtual PC
There are also dozens of providers of the Virtual Player which runs the OS in VM.
Virtual Box – Virtual Box is from Oracle, The most interesting thing about Virtual Box is that it is an independent platform with OS and hardware – it’s a Cross-platform Support. Cross-platform means you can run the Virtual Box on Intel system and also on AMD based system, no matter what the OS is – Windows Vista, XP, 7 or 8, you can even use RedHat Linux, Solaris, or Mac systems.
You can Download the Virtual box from: https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
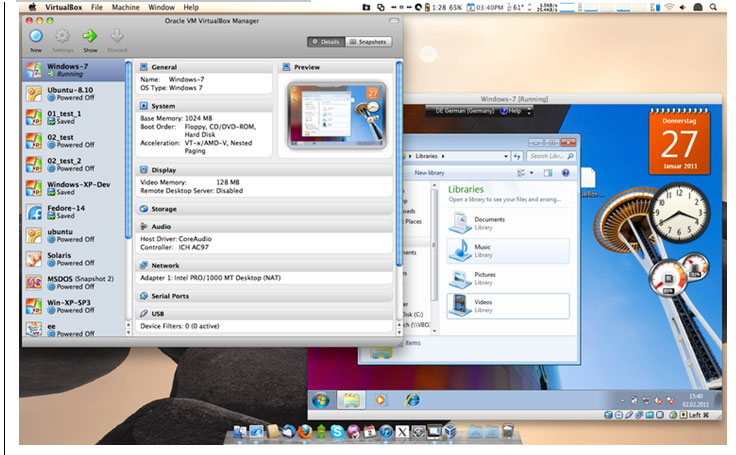
See Image 1.1 and 1.2.
1.1 Virtual Box
1.2 Virtual Box running in Windows 7
VMware: The big player of the Virtualization industry, it could be referred to as the Brand or Mark of Virtualization.
There are so many features and Big Player
nowadays. When you Visit the official Page of VMware you will findthat there are two possible downloadables
- Windows version
- Linux Version
Link for Download :
https://my.vmware.com/web/vmware/info/slug/desktop_end_user_computing/vmware_workstation/10_0
See Image 1.3
1.3 VMware Downloading
After installation, you can access the VMware software. In this tutorial, we are using VMware Workstation 9. There are a total of eight options in the menu, and we will look at each option in turn:
- Create a New Virtual Machine
- Open Virtual Machine
- Connect to a Remote Server
- Virtualize a Physical Machine
- Virtual Network Editor
- Workstations Preferences
- Software Updates
- Help
See Image 1.4