Router IOS Commands and Basic Router Configuration
Cisco Router IOS Commands and Basic Router Configurations
A Router is a Layer 3 device which is used to route packets from one network to the other. It uses the best path to route packets.
As we have an operating system on our Desktop computers and Servers e.g. Windows Server, Linux, Ubuntu etc, the Cisco devices also runs on an OS which is called the Internet working Operating System.
The IOS has a command line (CLI) interface where all the configurations to establish your network are done.
The IOS is stored in the memory area called flash.
The Flash memory is non-volatile in nature i.e. if the device loses power the contents remain intact and are not lost. The contents can however be changed or overwritten if required.
The router panel from behind would something like shown in below screenshot.
Ports
LAN Interface: FastEthernet
WAN Interface: Serial
Administrative: Console and AUX
Internal components of a Router
ROM: Read Only Memory: This is a chip on the motherboard which is coded with a bootstrap program which tells how the IOS should be loaded.
It starts and maintains the router. It contains the POST, mini-IOS and the Bootstrap program.
RAM: Random Access Memory: This holds the running or temporary config, the ARP cache, the routing tables and the software that help router to run.
It is also known as the running config. During boot, the IOS is loaded from the flash to the RAM
Flash Memory: the place where the IOS is actually stored. It DOES NOT erase when we reload the router.
NVRAM (Non Volatile RAM): This holds the configuration for router and switch. The IOS is not stored here, but the configuration register is stored here. NVRAM will not erase if a switch or router is reloaded.
POST: Power On Self-Test: This does automatically check the basic functionality of hardware for router and determines the interfaces present on it.
Mini-IOS: This is the boot loader or RXBOOT, provided by Cisco. This is a small IOS used to bring up and interface and help load the Cisco IOS into flash memory. It is stored in the ROM.
Configuration Register File: This controls how the router should boot up. Usually used while doing password recovery on router. The show version output shows this file. The default value set is 0x2102, which informs to load IOS from flash and to load the configuration to NVRAM
BOOT Sequence
POST: Identifies the hardware
ROM: Bootstrap Program is looked up from the ROM
Flash: IOS is loaded from the Flash
NVRAM: Flash contact NVRAM
RAM: NVRAM configuration is copied in RAM
Access Methods
The Cisco device CLI can be accessed using the following ways:
- Console
- SSH or Telnet
- AUX Port
Cisco IOS Modes
Cisco has different modes of operation in the CLI, which means depending on the mode you are capable of performing some actions on the device.
1. Setup Mode: It is the initial mode and a router would enter into this mode if the NVRAM does not contain any startup configuration. This is like a wizard where you do the initial configuration for your Cisco device. You can use the wizard or setup mode to do the configuration or can exit and get to another prompt or mode, which is called the user EXEC mode If you press ‘Yes’, you get a set of questions to be answered and have the device configured.
 If we type no, will go to the User Exec Mode
If we type no, will go to the User Exec Mode
 2. User EXEC Mode: This is the mode for basic commands mostly monitoring command also commonly known as ‘show’ commands in Cisco. Limited command such as ping, traceroute etc can be executed from User EXEC mode.The prompt is the ‘Greater than’ sign ‘>’.
2. User EXEC Mode: This is the mode for basic commands mostly monitoring command also commonly known as ‘show’ commands in Cisco. Limited command such as ping, traceroute etc can be executed from User EXEC mode.The prompt is the ‘Greater than’ sign ‘>’.
 After using ‘?’ we see the list of commands that can used, in this mode. This is known as context-sensitive help.
After using ‘?’ we see the list of commands that can used, in this mode. This is known as context-sensitive help.
3. Privileged Exec Mode or Enabled Mode: This mode is the advanced mode where all monitoring (show commands) and troubleshooting commands (debug commands) can be entered. Usually used by more experienced administrators.
This is mode similar to an administrator credential in the Windows or Linux System. We enter the command ‘enable’ to enter this mode. The ‘disable’ command takes you back from ‘enable mode’ to ‘User Exec Mode’
4. Global Configuration Mode: This mode is used to make any configuration changes on the device. Any changes done here will be applied to the router globally. E.g. hostname change.
You can enter configuration mode from the enable mode only, thus you have to have privileges of enable mode user. The command used to enter global config mode is “configure terminal’ or to make it short ‘config t’ from the privileged or enable mode.
To come back to the enabled prompt type ‘exit’ or ‘end’ or Ctrl+C.
 5. Specific Configuration Mode: (Interface / Line console): The commands entered in this mode affect only the specific part of the config in the router.
5. Specific Configuration Mode: (Interface / Line console): The commands entered in this mode affect only the specific part of the config in the router.
Interface Mode: In this mode configurations for interfaces are done, like configuring IP address, bring port / interface up down etc.
In the below screenshot we see router interface configuration mode. We configure the IP address for that particular interface
 See below the line console mode
See below the line console mode
6. ROMMON Mode: Used for password recovery Our topology that we will configure
See the screenshot below, on Packet Tracer, Click on the Admin PC and go to Desktop Tab. Click on Terminal and you see ‘terminal configurations’, similar configuration need to be set while using other applications (Putty, hyper Terminal) connected with console to router.
Click on OK and you get console access to the router. You come into the Setup Mode.
Enter ‘No’ to get directly into User Exec Mode.
Configure Hostname
 Imagine if you make a mistake in typing, the command or config. Cisco router will treat it as some domain name and try resolving it and give you the prompt after some time. This is very annoying.
Imagine if you make a mistake in typing, the command or config. Cisco router will treat it as some domain name and try resolving it and give you the prompt after some time. This is very annoying.
Configure no ip domain-lookup
You can turn this off by using “no ip domain-lookup”. If you enter any wrong command, you immediately get the error and the Router Prompt is ready to enter the command without delay.
Viewing interfaces on the router
 Assigning IP addresses to interfaces
Assigning IP addresses to interfaces
Also if you recheck the ‘show ip int brief’ you will see the IP address assigned on fa0/0 and the port is up.
Now the PCs can also pint the Router IP address (192.168.1.100)
Configure Console password
Here ‘line console 0’ means configuring for console port. The next line has the command ‘password’ and the actual password set for the console i.e. ‘console_pwd’. The ‘login’ keyword make the router prompt the user to key in a password. If we use ‘no login’ the user will not be prompted for password.
Configure Telnet password
To configure Telnet, you need to use the ‘line vty 0 4’ command, which means configure virtual terminal lines 0 through 4 i.e. 5 concurrent connections can be made using Telnet.
 The command ‘login’ prompts the user to enter the password. The password we set is ‘telnet_pwd’.
The command ‘login’ prompts the user to enter the password. The password we set is ‘telnet_pwd’.
Configure Enable or Privileged mode password
We configure the privileged mode password using the ‘enable password’ command
The password we set is ‘enable_pwd’.
Now that we have configured some passwords mentioned below, lets test them:
– Console password
– Enable password
– Telnet password
Exit out of the router and let it come to the initial screen share it shows ‘Press Return to get started’
Now see how the passwords are stored in the router. Issue the ‘show run’ command to see the running configuration. We see that all the passwords we configured are visible as clear text which is not a good thing in terms of security.
To overcome that flaw we will issue one more command.
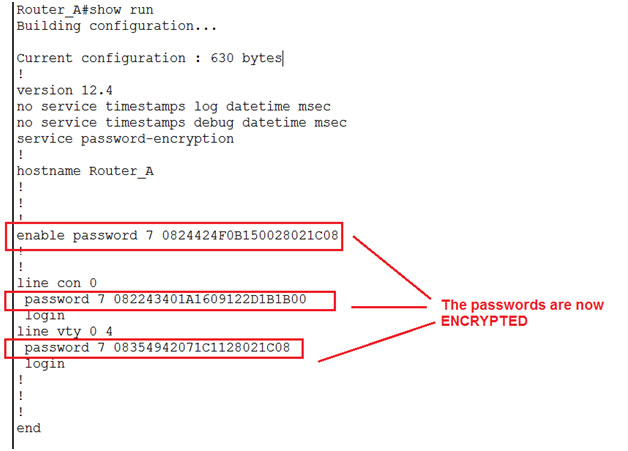
Encrypt passwords
We use the ‘over-shoulder’ algorithm. The command is ‘service password-encryption’.
Now again go to running config (show run) and check the config
To configure the Privileged mode with encrypted password while creating it, you can use the comman
Router(config)# enable secret enable_pwd_encrypt
Where ‘enable secret’ is the command and the remaining is the password which will be encrypted and saved.
Test the Telnet functionality, we see that we are being prompted to enter the password when we telnet form a PC to the router.
Save the configuration
We did the configurations recently which are stored in the running configuration, we need these to be save in the startup-config so next time we reboot the router we have all the configurations intact.
Time Configuration
We use the below command to see the time, and the remaining one to configure the new time. See screenshot.
The ‘show version’ command give some information about the IOS.
 It shows the software version, the system image file used, how much memory is available, the processor, cisco Router model and the configuration register.
It shows the software version, the system image file used, how much memory is available, the processor, cisco Router model and the configuration register.
Hope this has been of some help :)!!!
Read more
- What is IOS
- Router Memory
- Router Startup
- Understanding of Router Prompts
- Help Features of Router
- How to Configure Hostname, Clock and set banner on Cisco Router
- Configuring Fast Ethernet and Serial Interfaces on Cisco Router
- How to save router configurations
- How to set passwords on Cisco router
- How to Backup Cisco Router IOS
- Cisco Router Password Recovery
- Access Lists