InterVLAN Routing
InterVLAN Routing:
InterVLAN Routing is also called Router on a Stick . As we Know, that PCs on different VLAN Cannot communicate with each other, which means they can’t ping each other, since they are assigned to logically to different broadcasts. InterVLAN routing is done for them to communicate.
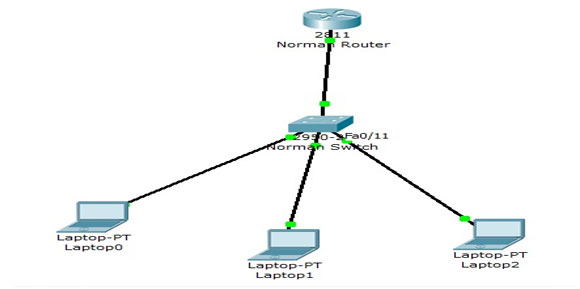
As shown in the figure below:Figure below
All these PCs are in three different VLANs, even though they can communicate through INterVLAN Routing.
Create three VLANs in Norman Switch, as explained in the first practical
Let’s say –
Developers: VLAN 10 : Ports F0/1-5
Marketing: VLAN 20 : Ports F0/6-10
Accounting: VLAN 30 : Ports F0/11-15
Configuring Switch
Switch> enable
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(Config)# hostname Norman_Switch
Norman_Switch(Config)# vlan 10
Norman_Switch(Config-vlan)# name Developers
Norman_Switch(Config)# exit
Norman_Switch(Config)# vlan 20
Norman_Switch(Config-vlan)# name Marketing
Norman_Switch(Config)# exit
Norman_Switch(Config)# vlan 30
Norman_Switch(Config-vlan)# name Accounts
Norman_Switch(Config)# exit
Norman_Switch(Config)# interface range f0/1-5
Norman_Switch(Config-if)# switchport mode access
Norman_Switch(Config-if)# switchport access vlan 10
Norman_Switch(Config-if)# exit
Norman_Switch(Config)# interface range f0/6-10
Norman_Switch(Config-if)# switchport mode access
Norman_Switch(Config-if)# switchport access vlan 20
Norman_Switch(Config-if)# exit
Norman_Switch(Config)# interface range f0/11-15
Norman_Switch(Config-if)# switchport mode access
Norman_Switch(Config-if)# switchport access vlan 30
Norman_Switch(Config-if)#exit
Norman_Switch(Config)# interface f0/24 (Trunk To Router)
Norman_Switch(Config-if)# switchport mode trunk
Norman_Switch(Config-if)#exit
Norman_Switch(Config)# do show vlan
Router Configuration
Router> enable
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# hostname Norman_Router
Norman_Router(Config)# interface f0/0
Norman_Router(Config-if)# no ip address
Norman_Router(Config-if)# no shutdown
Norman_Router(Config-if)#exit
Norman_Router(Config)# interface f0/0.1 (creating Sub interface)
Norman_Router(Config-if)# encapsulation dot1q 10 (10 is VLAN ID of Developers)
Norman_Router(Config-if)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Norman_Router(Config-if)# exit
Norman_Router(Config)# interface f0/0.2
Norman_Router(Config-if)# encapsulation dot1q 20
Norman_Router(Config-if)# ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
Norman_Router(Config-if)# exit
Norman_Router(Config)# interface f0/0.3
Norman_Router(Config-if)# encapsulation dot1q 30
Norman_Router(Config-if)# ip address 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.0
Norman_Router(Config-if)# exit
Assign the IP Address
Developers: 192.168.10.1-255
Marketing: 192.168.20.1-255
Accounts: 192.168.30.1-255
Ping from 192.168.10.1 to 192.168.30.1
C:\> ping 192.168.30.1
Pinging 192.168.30.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.30.1 :bytes=32 time=20ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.30.1 :bytes=32 time=20ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.30.1 :bytes=32 time=20ms TTL=254
Reply from 192.168.30.1 :bytes=32 time=20ms TTL=254
Ping Statistics for 192.168.30.1 :
Packets: Sent=4, Received=4 & Lost=0 (0% Loss)
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 10ms , Maximum = 20ms , Average = 15ms